BOJ_최솟값과 최댓값_2357 (Java)
BOJ_최솟값과 최댓값_2357 (Java)
[Gold I] 최솟값과 최댓값 - 2357
성능 요약
메모리: 58600 KB, 시간: 696 ms
분류
세그먼트 트리, 자료 구조
제출 일자
2024년 7월 31일 03:07:55
문제 설명
N(1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)개의 정수들이 있을 때, a번째 정수부터 b번째 정수까지 중에서 제일 작은 정수, 또는 제일 큰 정수를 찾는 것은 어려운 일이 아니다. 하지만 이와 같은 a, b의 쌍이 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 100,000)개 주어졌을 때는 어려운 문제가 된다. 이 문제를 해결해 보자.
여기서 a번째라는 것은 입력되는 순서로 a번째라는 이야기이다. 예를 들어 a=1, b=3이라면 입력된 순서대로 1번, 2번, 3번 정수 중에서 최소, 최댓값을 찾아야 한다. 각각의 정수들은 1이상 1,000,000,000이하의 값을 갖는다.
입력
첫째 줄에 N, M이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 N개의 정수가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 a, b의 쌍이 주어진다.
출력
M개의 줄에 입력받은 순서대로 각 a, b에 대한 답을 최솟값, 최댓값 순서로 출력한다.
## 문제 풀이
이전 풀었던 세그먼트 트리와 같다. 이전 학습하며 정리한 필기를 복기
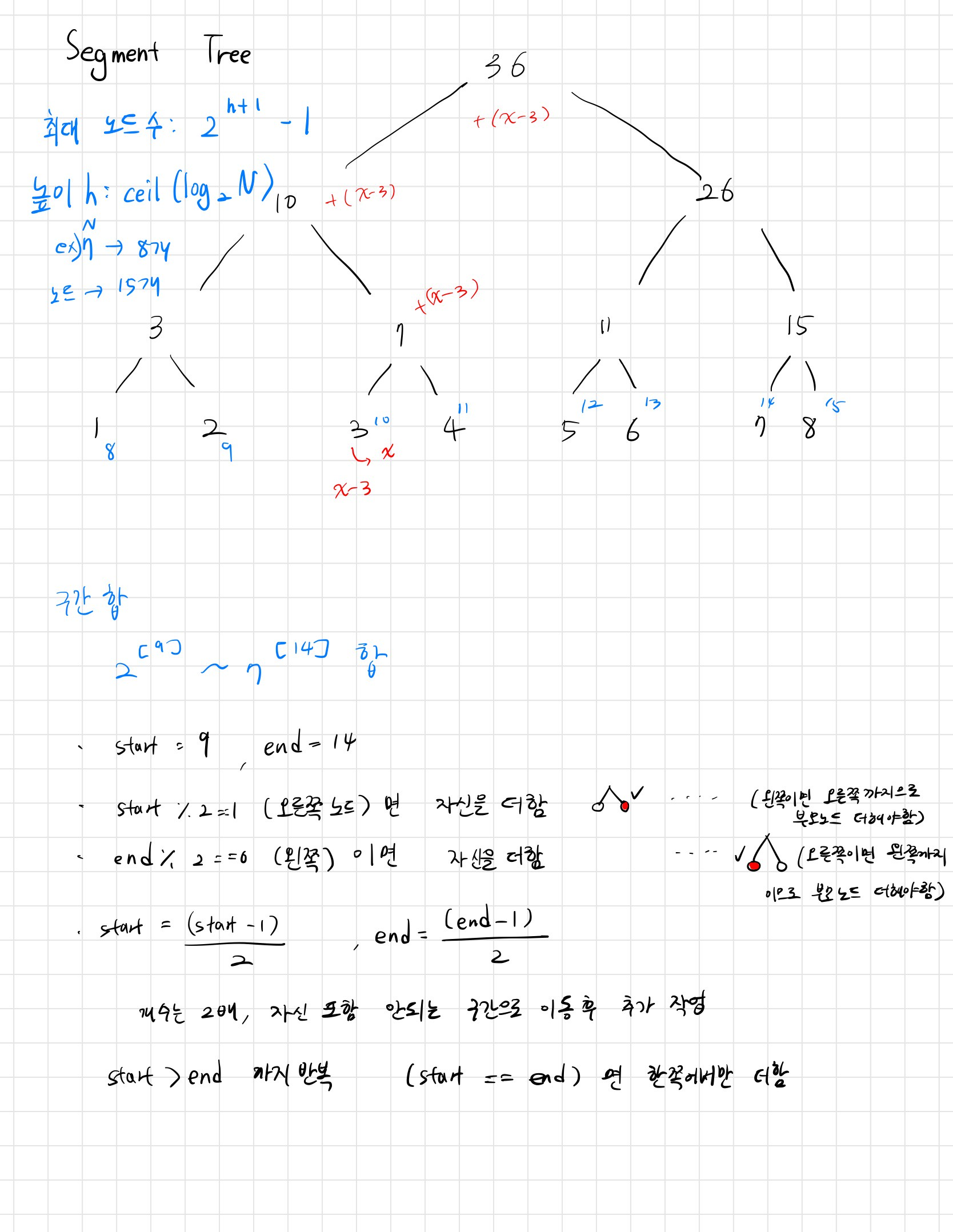
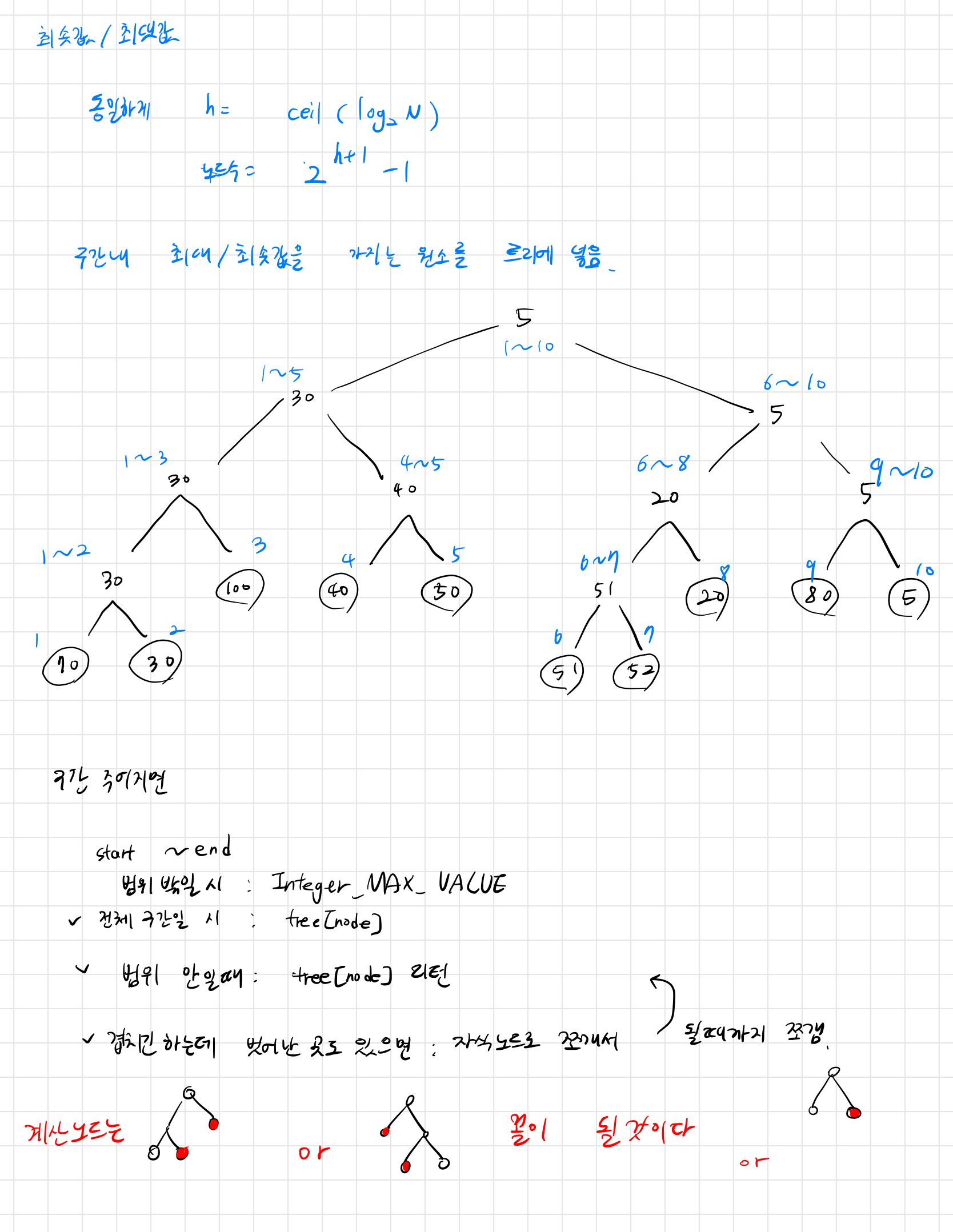

코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class BOJ_2357_최솟값과최댓값 {
static BufferedReader br;
static BufferedWriter bw;
static StringTokenizer st;
static int N, M;
static int[] minTree, maxTree, num;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("input.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int treeHeight = (int) Math.ceil(Math.log(N) / Math.log(2));
int treeSize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeHeight + 1) - 1;
minTree = new int[treeSize];
maxTree = new int[treeSize];
num = new int[N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
num[i] = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
initMinTree(1, N, 1);
initMaxTree(1, N, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
bw.write(getMin(1, N, 1, from, to) + " " + getMax(1, N, 1, from, to) + "\n");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
/*
* 세그먼트 트리 초기화
* node : 세그먼트 트리의 정점 번호
* start : 이 정점이 관리하는 연속 구간의 왼쪽 끝
* end : 이 정점이 관리하는 연속 구간의 오른쪽 끝
*
*/
private static int initMinTree(int start, int end, int node) { // 최솟값 트리
if (start == end) return minTree[node] = num[start];
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
return minTree[node] = Math.min(initMinTree(start, mid, node*2), initMinTree(mid + 1, end, node*2 + 1));
}
private static int initMaxTree(int start, int end, int node) { // 최댓값 트리
if (start == end) return maxTree[node] = num[start];
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
return maxTree[node] = Math.max(initMaxTree(start, mid, node*2), initMaxTree(mid + 1, end, node*2 + 1));
}
// from ~ to 구간 최솟값
private static int getMin(int start, int end, int node, int from, int to) {
// 보고있는 노드의 구간이 원하는 범위 밖인 경우
if (from > end || to < start) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 보고있는 노드의 구간이 원하는 범위 안인 경우
if (from <= start && to >= end) return minTree[node];
// 그 외 걸치는 경우는 재귀적으로 두 자식노드로 나눠서 최솟값 구하기
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
return Math.min(getMin(start, mid, node*2, from, to), getMin(mid + 1, end, node*2 + 1, from, to));
}
// from ~ to 구간 최댓값
private static int getMax(int start, int end, int node, int from, int to) {
// 보고있는 노드의 구간이 원하는 범위 밖인 경우
if (from > end || to < start) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// 보고있는 노드의 구간이 원하는 범위 안인 경우
if (from <= start && to >= end) return maxTree[node];
// 그 외 걸치는 경우는 재귀적으로 두 자식노드로 나눠서 최댓값 구하기
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
return Math.max(getMax(start, mid, node*2, from, to), getMax(mid + 1, end, node*2 + 1, from, to));
}
}
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.
