BOJ_1090_체커(Java, C++)
BOJ_1090_체커(Java, C++)
[Platinum IV] 체커 - 1090
성능 요약
메모리: 2024 KB, 시간: 4 ms
분류
브루트포스 알고리즘
제출 일자
2024년 12월 5일 23:23:08
문제 설명
N개의 체커가 엄청 큰 보드 위에 있다. i번 체커는 (xi, yi)에 있다. 같은 칸에 여러 체커가 있을 수도 있다. 체커를 한 번 움직이는 것은 그 체커를 위, 왼쪽, 오른쪽, 아래 중의 한 방향으로 한 칸 움직이는 것이다.
입력
첫째 줄에 N이 주어진다. N은 50보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 각 체커의 x좌표와 y좌표가 주어진다. 이 값은 1,000,000보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 수 N개를 출력한다. k번째 수는 적어도 k개의 체커가 같은 칸에 모이도록 체커를 이동해야 하는 최소 횟수이다.
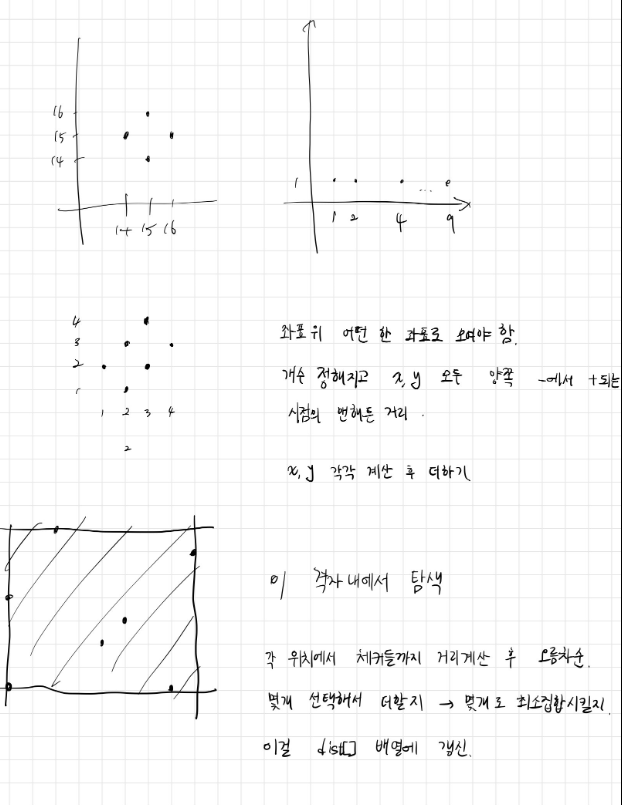
문제 풀이
생각보다 간단하게 풀렸다… 그냥 사실상 완전탐색.
코드
Java 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
class Checker{
int x;
int y;
Checker(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static BufferedReader br;
static BufferedWriter bw;
static StringTokenizer st;
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int N;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().solution();
}
public void solution() throws Exception {
// br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("input.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] x_arr = new int[N];
int[] y_arr = new int[N];
int[] dist = new int[N];
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Checker[] checker = new Checker[N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
x_arr[i] = x;
y_arr[i] = y;
checker[i] = new Checker(x, y);
}
List<Integer> distances = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0; i<x_arr.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<y_arr.length; j++) {
distances.clear();
int dis = 0;
for(Checker c : checker) {
distances.add(getDis(x_arr[i], y_arr[j], c));
}
Collections.sort(distances);
int cnt = 0;
for(int k=0; k<distances.size(); k++) {
cnt += distances.get(k);
dist[k] = Math.min(cnt, dist[k]);
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
sb.append(dist[i] + " ");
}
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
private int getDis(int i, int j, Checker c) {
return (int) Math.abs(i-c.x) + Math.abs(j-c.y);
}
}
C++ 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// #define int long long
#define MOD 1000000007
#define INF LLONG_MAX
#define ALL(v) v.begin(), v.end()
#ifdef LOCAL
#include "algo/debug.h"
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
class Checker {
public:
int x, y;
Checker(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
int getDis(int i, int j, Checker c) { return abs(i - c.x) + abs(j - c.y); }
void solve() {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<int> x_arr(N), y_arr(N), dist(N, INT_MAX);
vector<Checker> checkers;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
x_arr[i] = x;
y_arr[i] = y;
checkers.emplace_back(x, y); // 객체 생성과 동시에 삽입
}
for (int i = 0; i < x_arr.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y_arr.size(); j++) {
vector<int> distances;
for (auto& c : checkers) {
distances.push_back(getDis(x_arr[i], y_arr[j], c));
}
sort(ALL(distances));
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < distances.size(); k++) {
cnt += distances[k];
dist[k] = min(cnt, dist[k]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int tt = 1; // 기본적으로 1번의 테스트 케이스를 처리
// cin >> tt; // 테스트 케이스 수 입력 (필요 시)
while (tt--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.