BOJ_2096_내려가기 (Java, C++)
[Gold V] 내려가기 - 2096
성능 요약
메모리: 2020 KB, 시간: 20 ms
분류
다이나믹 프로그래밍, 슬라이딩 윈도우
제출 일자
2024년 12월 16일 17:03:41
문제 설명
N줄에 0 이상 9 이하의 숫자가 세 개씩 적혀 있다. 내려가기 게임을 하고 있는데, 이 게임은 첫 줄에서 시작해서 마지막 줄에서 끝나게 되는 놀이이다.
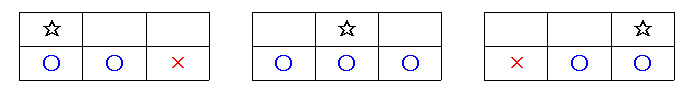
먼저 처음에 적혀 있는 세 개의 숫자 중에서 하나를 골라서 시작하게 된다. 그리고 다음 줄로 내려가는데, 다음 줄로 내려갈 때에는 다음과 같은 제약 조건이 있다. 바로 아래의 수로 넘어가거나, 아니면 바로 아래의 수와 붙어 있는 수로만 이동할 수 있다는 것이다. 이 제약 조건을 그림으로 나타내어 보면 다음과 같다.
별표는 현재 위치이고, 그 아랫 줄의 파란 동그라미는 원룡이가 다음 줄로 내려갈 수 있는 위치이며, 빨간 가위표는 원룡이가 내려갈 수 없는 위치가 된다. 숫자표가 주어져 있을 때, 얻을 수 있는 최대 점수, 최소 점수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. 점수는 원룡이가 위치한 곳의 수의 합이다.
입력
첫째 줄에 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 숫자가 세 개씩 주어진다. 숫자는 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 중의 하나가 된다.
출력
첫째 줄에 얻을 수 있는 최대 점수와 최소 점수를 띄어서 출력한다.
문제 풀이
간단한 dp 문제다. 자바로 풀 땐 dp배열과 board배열을 사용해 전체에 저장하며 풀었다. 이를 c++로 그대로 구현하니 메모리 초과가 발생했다. 이를 위해 전체적인 메모리 사용량을 줄여야했고 맨 처음 생각한 1차원dp (2차원에서 필요없는 이전 사용된값을 버리는) 방법을 채택했고 이에 그때그때 cin 값이 필요하므로 입력받고 dp계산하는식으로 반복했다.
코드
Java코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
package BOJ_2096_내려가기;
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader br;
static BufferedWriter bw;
static StringTokenizer st;
static int N, board[][], maxdp[][], mindp[][];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().solution();
}
public void solution() throws Exception {
// br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src/main/java/BOJ_2096_내려가기/input.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
board = new int[N][3];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
board[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
maxdp = new int[N + 1][3];
mindp = new int[N + 1][3];
maxdp[1][0] = mindp[1][0] = board[0][0];
maxdp[1][1] = mindp[1][1] = board[0][1];
maxdp[1][2] = mindp[1][2] = board[0][2];
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
maxdp[i][0] = board[i - 1][0] + Math.max(maxdp[i - 1][0], maxdp[i - 1][1]);
mindp[i][0] = board[i - 1][0] + Math.min(mindp[i - 1][0], mindp[i - 1][1]);
maxdp[i][1] = board[i - 1][1] + Math.max(maxdp[i - 1][0], Math.max(maxdp[i - 1][1], maxdp[i - 1][2]));
mindp[i][1] = board[i - 1][1] + Math.min(mindp[i - 1][0], Math.min(mindp[i - 1][1], mindp[i - 1][2]));
maxdp[i][2] = board[i - 1][2] + Math.max(maxdp[i - 1][1], maxdp[i - 1][2]);
mindp[i][2] = board[i - 1][2] + Math.min(mindp[i - 1][1], mindp[i - 1][2]);
}
int maxRes = Math.max(maxdp[N][0], Math.max(maxdp[N][1], maxdp[N][2]));
int minRes = Math.min(mindp[N][0], Math.min(mindp[N][1], mindp[N][2]));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(maxRes).append(" ").append(minRes);
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
C++ 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// #define int long long
#define MOD 1000000007
#define INF LLONG_MAX
#define ALL(v) v.begin(), v.end()
#ifdef LOCAL
#include "algo/debug.h"
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
void solve() {
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<int> maxdp(3), mindp(3);
vector<int> nextmaxdp(3), nextmindp(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int num;
cin >> num;
maxdp[i] = mindp[i] = num;
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
vector<int> tmp(3);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cin >> tmp[j];
}
nextmaxdp[0] = tmp[0] + max(maxdp[0], maxdp[1]);
nextmindp[0] = tmp[0] + min(mindp[0], mindp[1]);
nextmaxdp[1] = tmp[1] + max(maxdp[0], max(maxdp[1], maxdp[2]));
nextmindp[1] = tmp[1] + min(mindp[0], min(mindp[1], mindp[2]));
nextmaxdp[2] = tmp[2] + max(maxdp[1], maxdp[2]);
nextmindp[2] = tmp[2] + min(mindp[1], mindp[2]);
maxdp = nextmaxdp;
mindp = nextmindp;
}
int maxres = max(maxdp[0], max(maxdp[1], maxdp[2]));
int minres = min(mindp[0], min(mindp[1], mindp[2]));
cout << maxres << " " << minres << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int tt = 1; // 기본적으로 1번의 테스트 케이스를 처리
// cin >> tt; // 테스트 케이스 수 입력 (필요 시)
while (tt--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}