BOJ_2162_선분 그룹 (Java)
BOJ_2162_선분 그룹 (Java)
[Platinum V] 선분 그룹 - 2162
성능 요약
메모리: 19176 KB, 시간: 368 ms
분류
자료 구조, 분리 집합, 기하학, 선분 교차 판정
제출 일자
2024년 9월 22일 14:17:57
문제 설명
N개의 선분들이 2차원 평면상에 주어져 있다. 선분은 양 끝점의 x, y 좌표로 표현이 된다.
두 선분이 서로 만나는 경우에, 두 선분은 같은 그룹에 속한다고 정의하며, 그룹의 크기는 그 그룹에 속한 선분의 개수로 정의한다. 두 선분이 만난다는 것은 선분의 끝점을 스치듯이 만나는 경우도 포함하는 것으로 한다.
N개의 선분들이 주어졌을 때, 이 선분들은 총 몇 개의 그룹으로 되어 있을까? 또, 가장 크기가 큰 그룹에 속한 선분의 개수는 몇 개일까? 이 두 가지를 구하는 프로그램을 작성해 보자.
입력
첫째 줄에 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 3,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N+1번째 줄에는 양 끝점의 좌표가 x1, y1, x2, y2의 순서로 주어진다. 각 좌표의 절댓값은 5,000을 넘지 않으며, 입력되는 좌표 사이에는 빈칸이 하나 있다.
출력
첫째 줄에 그룹의 수를, 둘째 줄에 가장 크기가 큰 그룹에 속한 선분의 개수를 출력한다.
문제 풀이
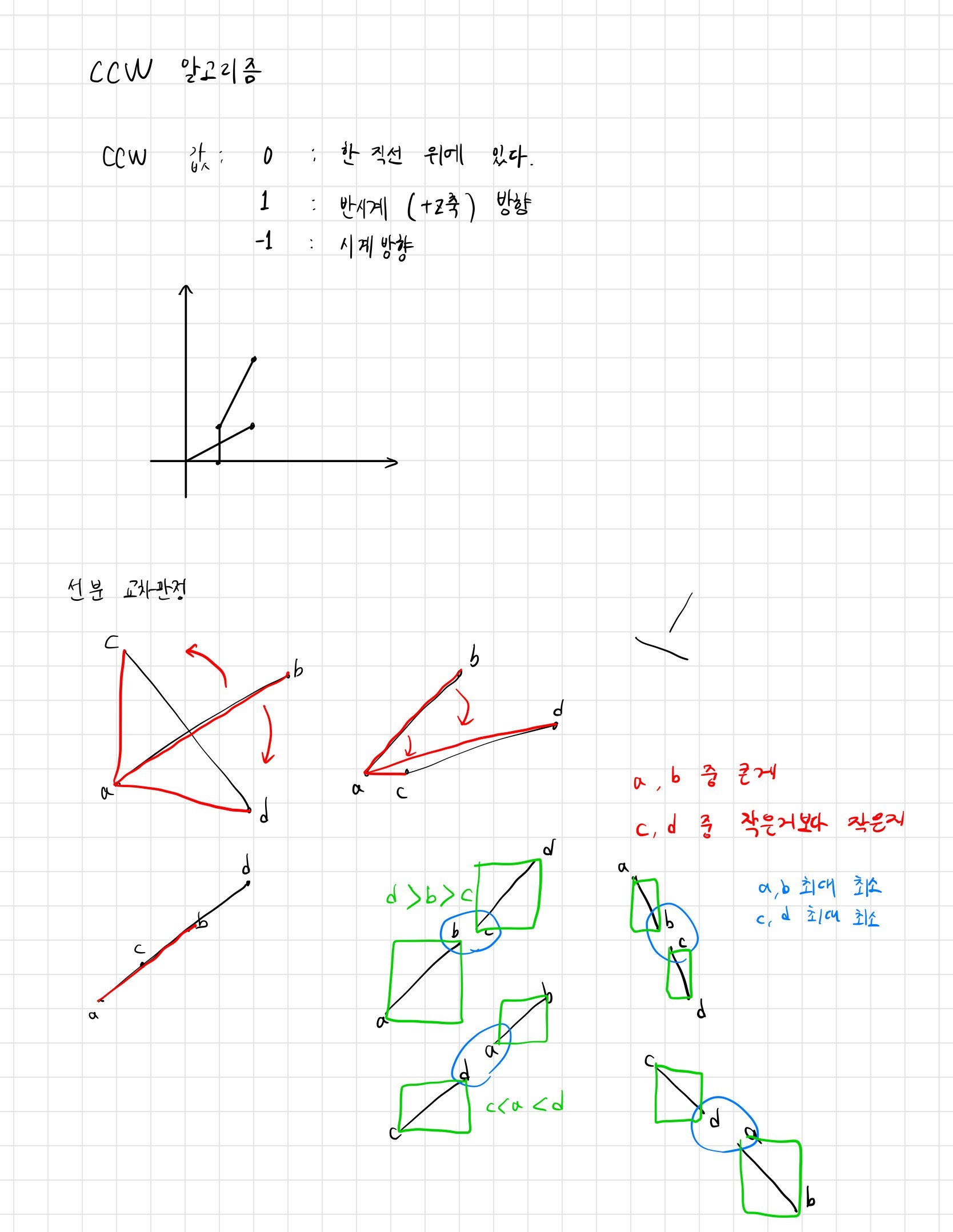
 풀이 방법은 쉽게 떠올렸지만 케이스 처리 부분에서 생각을 오래했던 문제. 일자로 두 선분이 나란히 있을때 어떻게 처리해야할 지 , 동 떨어져 있던 두 선분이 새로운 선분에 의해 한 그룹으로 바뀔 때 ( ㅣㅣ 에서 ㅐ 모양 같이 ) 어떻게 처리 할 지 고민을 많이 했다.
경로압축 및 분리집합, 벡터 외적 스칼라곱을 활용해 풀었다.
풀이 방법은 쉽게 떠올렸지만 케이스 처리 부분에서 생각을 오래했던 문제. 일자로 두 선분이 나란히 있을때 어떻게 처리해야할 지 , 동 떨어져 있던 두 선분이 새로운 선분에 의해 한 그룹으로 바뀔 때 ( ㅣㅣ 에서 ㅐ 모양 같이 ) 어떻게 처리 할 지 고민을 많이 했다.
경로압축 및 분리집합, 벡터 외적 스칼라곱을 활용해 풀었다.
코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader br;
static BufferedWriter bw;
static StringTokenizer st;
static int N;
static Line[] lines;
static Group[] groups;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().solution();
}
public void solution() throws Exception {
// br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("input.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
lines = new Line[N];
groups = new Group[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int x2 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y2 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lines[i] = new Line(x1, y1, x2, y2);
groups[i] = new Group(i);
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=i+1; j<N; j++) {
if(isLineCrossed(lines[i], lines[j])) union(i, j);
}
}
int groutCnt = 0;
int maxSize = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
if(groups[i].parent == i) {
groutCnt++;
maxSize = Math.max(maxSize, groups[i].size);
}
}
bw.write(groutCnt + "\n" + maxSize);
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
private int find(int start) {
if(groups[start].parent != start) groups[start].parent = find(groups[start].parent);
return groups[start].parent;
}
private void union(int start, int end) {
int root1 = find(start);
int root2 = find(end);
if(root1 != root2) {
if (groups[root1].size < groups[root2].size) { // 그룹2에 1을 포함시키기
groups[root1].parent = root2;
groups[root2].size += groups[root1].size;
} else { // 그룹1에 2을 포함시키기
groups[root2].parent = root1;
groups[root1].size += groups[root2].size;
}
}
}
private static int ccw(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) {
long res = (p1.x * p2.y + p2.x * p3.y + p3.x * p1.y) - (p1.x * p3.y + p3.x * p2.y + p2.x * p1.y);
if(res == 0) return 0;
else if (res > 0) return 1;
else return -1;
}
private static boolean isLineCrossed(Line l1, Line l2) {
Point p1 = l1.p1;
Point p2 = l1.p2;
Point p3 = l2.p1;
Point p4 = l2.p2;
int ccw1 = ccw(p1, p2, p3) * ccw(p1, p2, p4);
int ccw2 = ccw(p3, p4, p1) * ccw(p3, p4, p2);
// 1. 한 줄 일때
// 1 3 2 4 처럼 겹칠텐데 1<4 고 2>3 임을 수식으로 작성
if (ccw1 == 0 && ccw2 == 0) {
if (Math.min(p1.x, p2.x) <= Math.max(p3.x, p4.x) &&
Math.min(p3.x, p4.x) <= Math.max(p1.x, p2.x) &&
Math.min(p1.y, p2.y) <= Math.max(p3.y, p4.y) &&
Math.min(p3.y, p4.y) <= Math.max(p1.y, p2.y)) {
return true;
}
else return false;
}
// 2. 크로스가 있을 가능성이 있을 때
// 2-1. 둘 다 ccw 곱이 음수면 완전 크로스 : true
else if (ccw1 <= 0 && ccw2 <= 0) return true;
// 그 외는 한쪽 음수 한쪽 양수이므로 ㅡ ㅣ 같은 모양임 : false
else return false;
}
class Point implements Comparable<Point>{
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Point o) {
if(this.x == o.x) return this.y - o.y;
return this.x - o.x;
}
}
class Line{
Point p1, p2;
public Line(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
Point point1 = new Point(x1, y1);
Point point2 = new Point(x2, y2);
p1 = point1.compareTo(point2) <= 0 ? point1 : point2;
p2 = point1.compareTo(point2) <= 0 ? point2 : point1;
}
}
class Group{
int parent;
int size;
public Group(int parent) {
this.parent = parent;
this.size = 1;
}
}
}
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.
