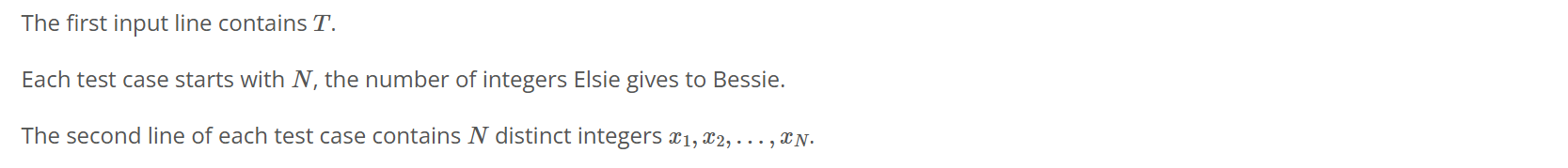BOJ_21818_Do You Know Your ABCs?
BOJ_21818_Do You Know Your ABCs?
[Platinum V] Do You Know Your ABCs? - 21818
성능 요약
메모리: 21520 KB, 시간: 204 ms
분류
브루트포스 알고리즘, 구현, 수학
제출 일자
2024년 11월 18일 03:51:48
문제 설명
입력
출력
For each test case, output the number of triples $(A,B,C)$ that are consistent with the numbers Elsie presented.
문제 풀이
코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader br;
static BufferedWriter bw;
static StringTokenizer st;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().solution();
}
public void solution() throws Exception {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("input.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
while(T-->0) {
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] arr = new int[N+1];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
int res = solve(arr, N);
bw.write(String.valueOf(res) + "\n");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
/**
* A, B, C 가능한 숫자 찾기
* 숫자 찾은 후 가능한 경우의 수 리턴
*
* @param arr
* @param n
* @return 가능한 조합 경우의 수
*/
private int solve(int[] arr, int N) {
Set<Integer> nums = new HashSet<Integer>(); // N개의 숫자 가능 후보
for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) {
for(int j=i+1; j<=N; j++) {
// 각 값 + 0끼리의 차이
int diff = Math.abs(arr[j] - arr[i]);
if(diff>0) nums.add(diff);
}
}
int cnt = 0;
for(int A : nums) {
for(int B : nums) {
for(int C : nums) {
if(A>B || B>C) continue; // 1<=A<=B<=C
if(isAns(A, B, C, arr, N)) cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
private boolean isAns(int A, int B, int C, int[] arr, int N) {
int A_plus_B = A+B;
int B_plus_C = B+C;
int C_plus_A = C+A;
int A_plus_B_plus_C = A+B+C;
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
if(arr[i] != A &&
arr[i] != B &&
arr[i] != C &&
arr[i] != A_plus_B &&
arr[i] != B_plus_C &&
arr[i] != C_plus_A &&
arr[i] != A_plus_B_plus_C) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.