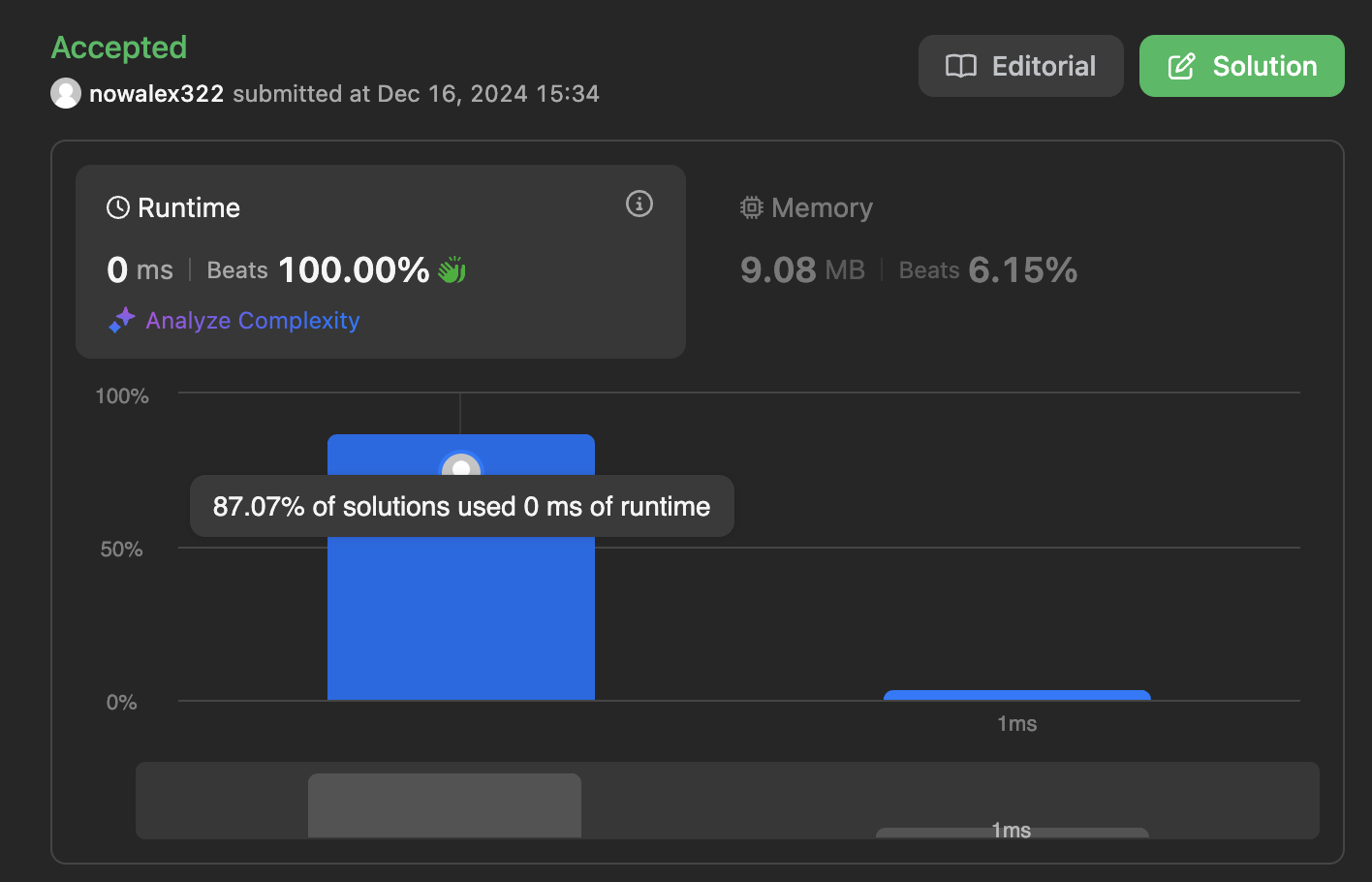
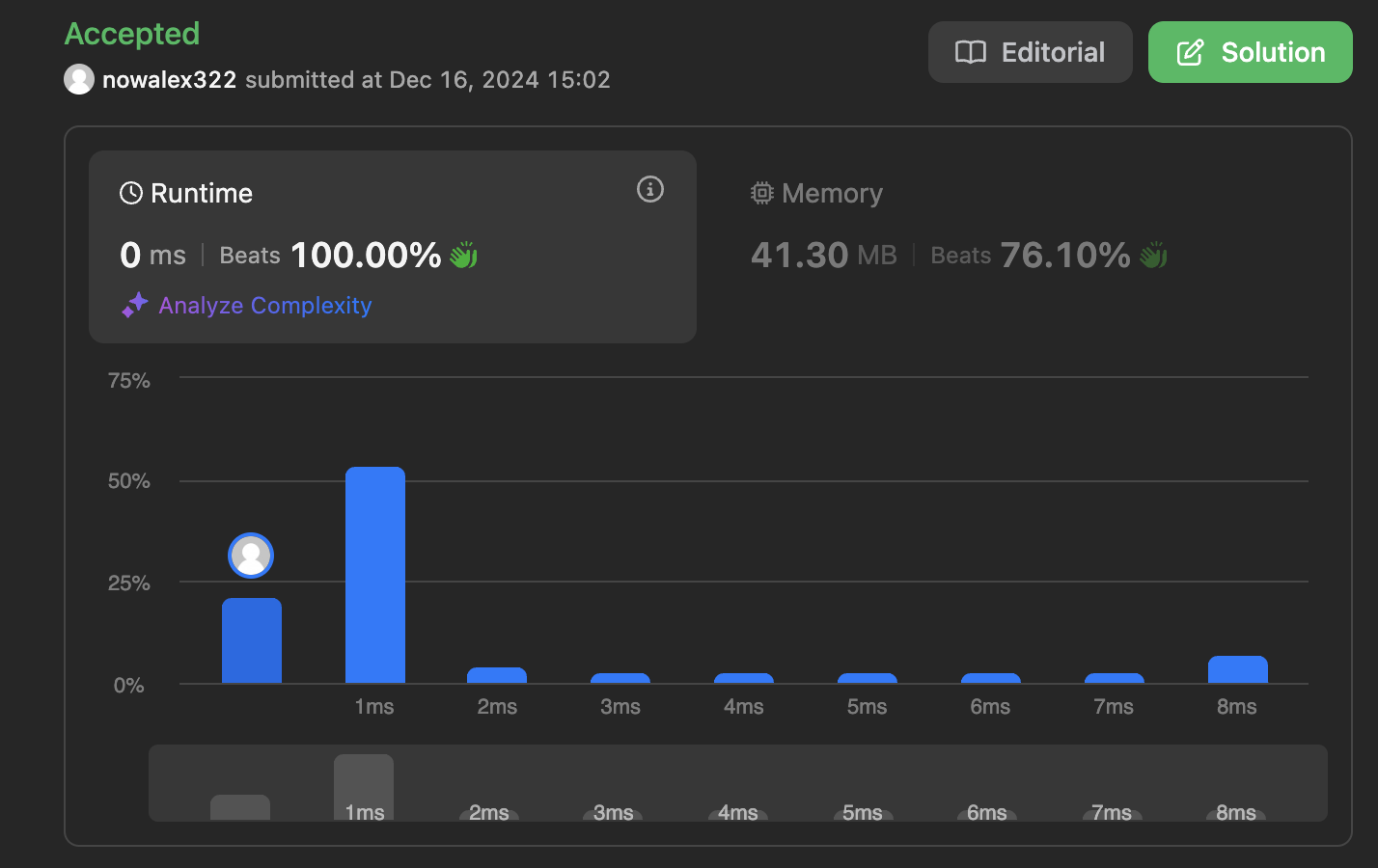
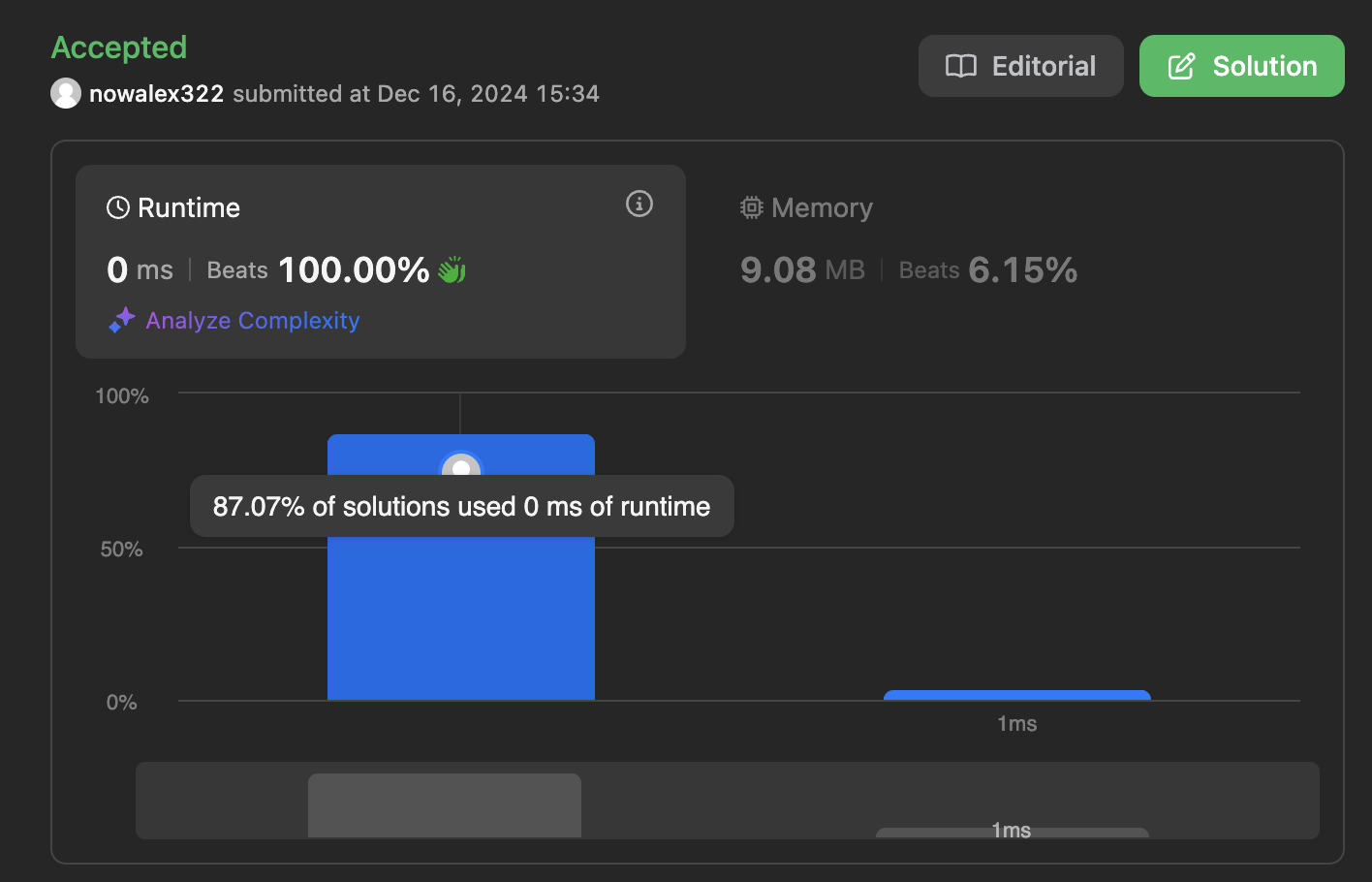
LeetCode_433_Minimum Genetic Mutation (Java, C++)
433. Minimum Genetic Mutation
Medium
A gene string can be represented by an 8-character long string, with choices from 'A', 'C', 'G', and 'T'.
Suppose we need to investigate a mutation from a gene string startGene to a gene string endGene where one mutation is defined as one single character changed in the gene string.
- For example,
"AACCGGTT" --> "AACCGGTA"is one mutation.
There is also a gene bank bank that records all the valid gene mutations. A gene must be in bank to make it a valid gene string.
Given the two gene strings startGene and endGene and the gene bank bank, return the minimum number of mutations needed to mutate from startGene to endGene. If there is no such a mutation, return -1.
Note that the starting point is assumed to be valid, so it might not be included in the bank.
Example 1:
Input: startGene = "AACCGGTT", endGene = "AACCGGTA", bank = ["AACCGGTA"] Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: startGene = "AACCGGTT", endGene = "AAACGGTA", bank = ["AACCGGTA","AACCGCTA","AAACGGTA"] Output: 2
Constraints:
0 <= bank.length <= 10startGene.length == endGene.length == bank[i].length == 8startGene,endGene, andbank[i]consist of only the characters['A', 'C', 'G', 'T'].
문제 풀이
완전 탐색을 생각했다. 이후 어떻게 찾은 문자에 대해서만 진행하지를 생각했을 때 queue에 넣고 그 사이즈만큼 반복해서 돌리면 될 것 같았다. BFS알고리즘과 비슷한 것 같다.
이후 어떻게 이 gene들을 비교할 지 생각 중 문자열이기 때문에 contains를 사용시 O(8)만큼 걸리는데 이를 사칙연산인 ==을 사용한다면 O(1)이 걸릴것이기 때문에 A, C, G, T 를 각각 1, 2, 3, 4로 해싱한 뒤 10진수로 바꿔 고유의 유전자 패턴을 만들어줬다.
개선점은 List의 contains메서드는 list의 길이만큼 순회해야 하기 때문에 O(N)의 시간복잡도를 가지는데 HashSet의 경우 hashTable로 구현되어있기 때문에 key-value형태를 가지고 있고 이를 hashMap.contains() 메서드를 사용하기 때문에 O(1)의 시간복잡도를 가진다고 한다. 이에 visited의 자료구조를 List에서 hashSet으로 변경하였다.
c++의 경우 알고리즘 라이브러리의 find함수를 통해 vector이나 list에서 값을 찾는데 이때 찾으면 그 찾은 iterator을 반환하고, 못찾으면 해당 자료구조의 .end()를 반환한다고 한다.그리고 unordered_set과 set에서 contains함수를 c++20부터 쓸 수 있다고 한다.
코드
Java 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
class Solution {
public int minMutation(String startGene, String endGene, String[] bank) {
int start = hashing(startGene);
int end = hashing(endGene);
List<Integer> geneBank = new ArrayList<>();
for(String s : bank){
geneBank.add(hashing(s));
}
if(!geneBank.contains(end)) return -1;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.offer(start);
visited.add(start);
int cnt = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int s = 0; s < size; s++){
int curr = queue.poll();
if(curr == end) return cnt;
for(int idx = 0; idx < 8; idx++){
int idxNum = curr/ (int) Math.pow(10, idx) % 10;
for(int newNum= 1; newNum <= 4; newNum++){
if(idxNum != newNum) {
int next = curr + (newNum - idxNum) * (int) Math.pow(10, idx);
if(geneBank.contains(next) && !visited.contains(next)){
queue.offer(next);
visited.add(next);
}
}
}
}
}
cnt++;
}
return -1;
}
private int hashing(String str){ // 10진수 해싱
int num = 0;
for(int i=0; i<8; i++){
num *= 10;
char c = str.charAt(i);
if(c=='A') num += 1;
else if(c=='C') num += 2;
else if(c=='G') num += 3;
else num += 4;
}
return num;
}
}
C++ 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
#define ALL(v) v.begin(), v.end()
class Solution {
public:
int minMutation(string startGene, string endGene, vector<string>& bank) {
int start = hashing(startGene);
int end = hashing(endGene);
vector<int> geneBank;
for(string s : bank){
geneBank.push_back(hashing(s));
}
if(find(ALL(geneBank), end) == geneBank.end()) return -1;
queue<int> queue;
unordered_set<int> visited;
queue.push(start);
visited.insert(start);
int cnt = 0;
while(!queue.empty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int s=0; s<size; s++){
int curr = queue.front();
queue.pop();
if(curr == end) return cnt;
for(int idx = 0; idx<8; idx++){
int idxNum = curr / (int) pow(10, idx) % 10;
for(int newNum=1; newNum <= 4; newNum++){
if(idxNum != newNum) {
int next = curr + (newNum - idxNum) * (int)pow(10, idx);
if(find(ALL(geneBank), next) != geneBank.end() && !visited.contains(next)){
queue.push(next);
visited.insert(next);
}
}
}
}
}
cnt++;
}
return -1;
}
private:
int hashing(string str){
int num = 0;
for(int i=0; i<8; i++){
num *= 10;
char c = str[i];
if(c=='A') num += 1;
else if(c=='C') num += 2;
else if(c=='G') num += 3;
else num += 4;
}
return num;
}
};